Kelsey Robinson, 2026 PharmD Candidate, Idaho State University
“Is this medication gluten free?”
It’s not a question you hear every day at the pharmacy counter. But for the patients who ask, often those with celiac disease, the answer can mean the difference between health and harm. Pharmacists are often the last line of defense, and in these moments, our knowledge truly matters.
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease affects 1 in 100 people worldwide. It’s a serious autoimmune condition that damages the small intestine when gluten is ingested. Symptoms vary widely and may include abdominal pain, bloating, constipation or diarrhea, fatigue, skin rashes, and cognitive issues. Some patients are even asymptomatic, making diagnosis and treatment even more complex.

Why skip gluten?
Currently, the only effective treatment for celiac disease is a 100% gluten free diet. Avoiding gluten can be difficult enough in food, let alone in unexpected places like prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medications. Manufacturers are not required to disclose gluten content in drug products, and most do not include labeling to help guide patients or providers.
The Evasive Excipient.
Even if the active drug is gluten-free, hidden ingredients, known as excipients, may still pose a risk. Prescription drugs and supplements are formulated with excipients to stabilize or bind ingredients, improve absorption, or enhance shelf life. Common excipients that may contain gluten include:
Starch
Pre-gelatinized starch
Dextrates
Dextrin
Dextrimaltose
Cyclodextrins
Maltodextrin
Sodium starch glycolate
How can the pharmacist help?
With no labeling requirements in place, pharmacists are uniquely positioned to advocate for celiac and gluten-sensitive patients. While we may have access to drug databases and manufacturer resources, patients also benefit from these publicly available tools:
www.glutenfreedrugs.com
*I believe it is important to note that this list has not be updated since 2019.
dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/
https://www.fda.gov/media/116958/download
Some questions pharmacists can ask manufacturers when verifying gluten status:
- Is wheat, barley, or rye used in any part of the formulation?
- Are any excipients derived from gluten-containing grains?
- Do you batch-test for gluten content?
- Is there potential for cross-contamination during manufacturing?
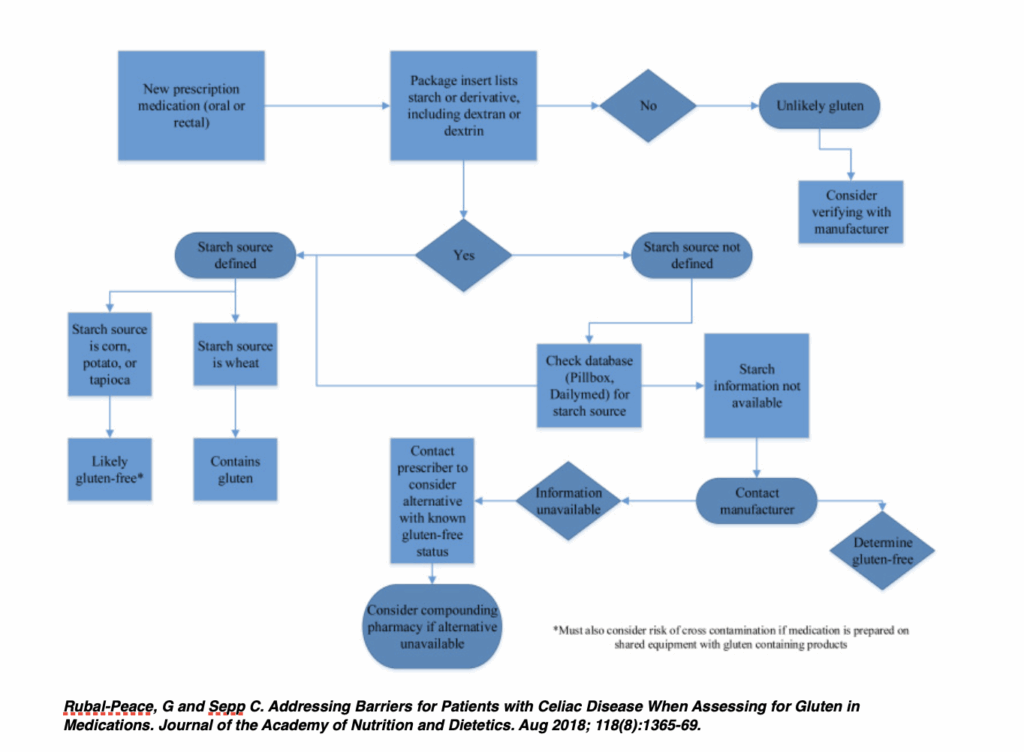
The flowchart below was created by a pharmacist to help identify the gluten content of medications:
Supplement Safety.
Supplement safety is another concern frequently raised by patients. I spoke with Dr. Courtenay Newton, N.D., of Madison Park Pharmacy & Wellness Center in Seattle, WA, who recommends patients look for reputable brands who prioritize mitigating cross-contamination, batch-test, and clearly label gluten-free status. When in doubt, patients, or pharmacists, should contact the manufacturer directly to verify.
Final Thoughts: Small Details, Big Impact
For patients with celiac disease, the burden of constantly avoiding gluten can be overwhelming. The last thing we want is to unknowingly expose them through a medication or OTC product.
Pharmacists are in a powerful position to protect patients with celiac disease. By staying informed, asking the right questions, and guiding patients toward trusted resources, we can eliminate hidden risks and strengthen trust where it matters most.

